Four Models
Possible Real-life Meanings of - Random Variable
- Time to event
- Survival time after cancer diagnosis
- Time in remission
- Recovery time after surgery
- Dollar amount of an auto insurance claim
- Dollar payment on a medical malpractice policy in one year
- Number of claims submitted in six months
Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF)
Definition
The cumulative ditribution function is also called the distribution function. It is usually denotes as or , for a random variable . It represents the probability that is less than or equal to a given number. That is . The abbreviation cdf is often used.
Non-decreasing
Right-continuous
,
Survival Function
Definition
The survival function, usually denoted as or , for a random variable is the probability that is greater than a given number. That is,
Non-increasing
Right-continuous
,
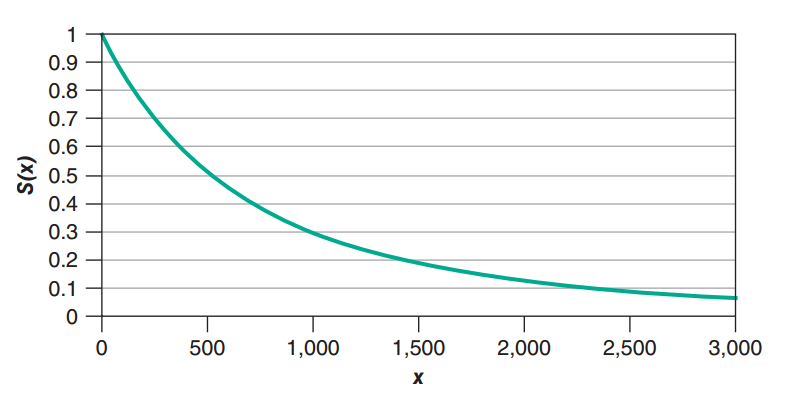
Exponential Survival Function
Probability Density Function (PDF)
if derivative exists
Hazard Function
Cumulative Hazard